9.5 KiB
9.5 KiB
- #CT230 - Database Systems I
- Previous Topic: Database System Introduction
- Next Topic: Introduction to SQL & DDL
- Relevant Slides:
- Why learn about relational DBMS?
- 90% of industry / enterprise / business applications are still relational DBMS or relational DBMS with extensions (e.g., OO Relational).
- The majority of industry applications require:
- Correctness
- Completeness
- Efficiency (Complex optimisation techniques & complex indexing structures).
- Relational DBMS provide this.
- What is the Relational Data Model? #card
card-last-interval:: 21.53
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-06T08:01:57.584Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:01:57.584Z
card-last-score:: 3
- The Relational Data Model consists of collections of relations (often called tables) where each relation contains tuples (rows) and attributes (columns).
- The relational data model is closely related to the file system model.
- Relations are named.
- What is a relation? #card
card-last-interval:: 31.36
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.8
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-20T16:24:50.257Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-20T08:24:50.257Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A table.
- What are attributes? #card
card-last-interval:: 100.92
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2023-02-23T18:22:23.155Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:22:23.156Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Attributes are columns.
- Columns / attributes are ^^almost always fixed^^ and do not change.
- What are tuples? #card
card-last-interval:: 29.26
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T22:48:34.835Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:48:34.835Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Tuples are rows.
- Rows contain the data.
- There is a variable number of rows.
- What is the cardinality of a relation? #card
card-last-interval:: -1
card-repeats:: 1
card-ease-factor:: 2.8
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-15T00:00:00.000Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:51:27.460Z
card-last-score:: 1
- The ^^number of tuples in a relation^^ is referred to as the cardinality of that relation.
-
Attributes / Columns
- Each attribute belongs to one domain and has a single:
- Name
- Data Type
- Format
-
Naming Columns #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3 card-repeats:: 4 card-ease-factor:: 2.66 card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-17T15:34:15.662Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-20T08:34:15.663Z card-last-score:: 5- Case is not significant in SQL.
- No spaces allowed.
- No reserved keywords (e.g., date) allowed.
- Choose meaningful variable names.
- If given the names of relations and attributes, use ^^exactly^^ what you are given.
-
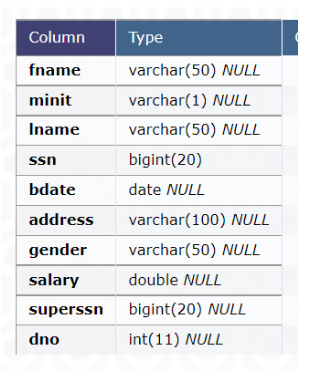
Data Types
- You must ^^specify the data type^^ of all attributes (columns) defined.
- Common data types used include:
- varchar(N), where N is an integer - used for strings.
- date
- int
- double
- You often must specify the size - especially for integers and strings
-
NULL
- What are null-valued attributes? #card
card-last-interval:: 29.26
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T22:48:31.350Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:48:31.350Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Null-valued attributes are what occurs when the values of some attribute within a particular tuple may be unknown or may not apply to that particular tuple. A null value is used for these cases.
- NULL is a special marker used in SQL to denote the ^^absence of a value.^^
- In some cases, we wish to allow the possibility of a
NULLvalue although they will often require extra handling (e.g., checkingif == NULL). - In other cases, we want to prevent
NULLfrom being entered as a value and specifyNOT NULLas a constraint on data entry.
- What are null-valued attributes? #card
card-last-interval:: 29.26
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T22:48:31.350Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:48:31.350Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Atomic Attributes
- What is an atomic attribute? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:51:31.019Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:51:31.019Z
card-last-score:: 5
- An atomic attribute is an attribute which contains a ^^single value of the appropriate type^^, generally meaning, "no repeating values of the same type".
- The relational model should only have atomic values.
- What is an atomic attribute? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:51:31.019Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:51:31.019Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Composite Attributes
- What is a composite attribute? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:52:00.872Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:52:00.872Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A composite attribute is an attribute that is composed of several atomic attributes.
- E.g.,
Name = FirstName, Middle Initial, Surname.
- E.g.,
- We often want to decompose a composite attribute into atomic attributes unless there is a very good reason not to.
- A composite attribute is an attribute that is composed of several atomic attributes.
- What is a composite attribute? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:52:00.872Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:52:00.872Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Multi-Valued Attributes
- What is a multi-valued attribute? #card
card-last-interval:: 4.14
card-repeats:: 2
card-ease-factor:: 2.56
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-26T16:37:36.766Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-22T13:37:36.767Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A multi-valued attribute is an attribute which has lower and upper bounds on the number of values for an individual entry.
- The ^^opposite of an atomic attribute.^^
- The relational model should not store multi-valued attributes.
- Database design / redesign should be used to deal with this issue by creating more attributes (columns) or more tables.
- A multi-valued attribute is an attribute which has lower and upper bounds on the number of values for an individual entry.
-
Derived Attributes
- What are derived attributes? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-12T23:52:22.646Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:52:22.646Z
card-last-score:: 3
- A derived attribute is an attribute whose value can be determined from another attribute.
- E.g., you can derive age from birthdate.
- It is a good idea to not directly store attribute which can be derived from other attributes.
- A derived attribute is an attribute whose value can be determined from another attribute.
- What are derived attributes? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-12T23:52:22.646Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:52:22.646Z
card-last-score:: 3
- What is a multi-valued attribute? #card
card-last-interval:: 4.14
card-repeats:: 2
card-ease-factor:: 2.56
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-26T16:37:36.766Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-22T13:37:36.767Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Each attribute belongs to one domain and has a single:
-
Collection of Relations
- A Relational Data Model consists of a collection of relations (tables).
- Tables are cross-linked.
- A Relational Data Model consists of a collection of relations (tables).
-
- A relational database usually contains many relations (tables) rather than storing all data in one single relation.
- What is a Relational Schema? #card
card-last-interval:: 19.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-04T03:03:56.818Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:03:56.818Z
card-last-score:: 3
- A relational schema,
R, is the ^^definition of a table in the database.^^ It can be denoted by listing the table name and the attributes:-
R=\{A_1,A_2,...,A_n\}- where
A_iis an attribute.
- where
- E.g., with
n=3,works_on(essn, pno, hours).
-
- A relational schema,
-
Linking Tables
- Two ^^extremely important concepts^^ within the relational model which allows tables to be linked & cross-referenced are:
- Primary Key attributes.
- Foreign Key attributes.
-
Primary Keys
- Fundamental concept of Primary Keys: #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-17T15:34:03.291Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-20T08:34:03.291Z
card-last-score:: 5
- ^^All tuples (rows) in a relation must be distinct.^^
- To ensure this, we must have one or more attributes / columns whose data values will ^^always be unique for each tuple^^ - these attributes are called key attributes and are used to identify a tuple in the relation.
- There may be a few possibilities for the primary key - these are called Candidate Keys.
- One candidate key is ultimately chosen as the primary key during the Design Stage.
- What is a Primary Key? #card
card-last-interval:: 23.43
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-08T02:44:46.959Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:44:46.960Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A primary key is defined as one or more attributes per table where:
- there can only be one such primary key per table
- the primary key can never contain the
NULLvalue - all values entered for the primary key must be unique (no duplicates across the rows)
- Often, primary keys are used as indices.
- We use the convention (in writing) that attribute which form primary keys are
\text{\underline{underlined}}.
- A primary key is defined as one or more attributes per table where:
- Fundamental concept of Primary Keys: #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-17T15:34:03.291Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-20T08:34:03.291Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Foreign Keys
- What is a Foreign Key? #card
card-last-interval:: 23.43
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-08T02:52:18.585Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:52:18.585Z
card-last-score:: 3
- A Foreign Key is an attribute, or a set of attributes, within one table that matches or links to a candidate key of some other table (possibly the same table).
- More formally:
- Given relations
r_1andr_2, a foreign key ofr_2is an attribute (or set of attributes) inr_2where that attribute is a candidate key inr_1. Relationsr_1andr_2may be the same relations.
- Given relations
-
Foreign Key Terminology
- The parent, master, or referenced table is the relation containing the candidate key(s).
- The child or referencing table / relation is the relation containing the foreign key.
- What is a Foreign Key? #card
card-last-interval:: 23.43
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-08T02:52:18.585Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:52:18.585Z
card-last-score:: 3
- Two ^^extremely important concepts^^ within the relational model which allows tables to be linked & cross-referenced are:
