26 KiB
26 KiB
- #CT213 - Computer Systems & Organisation
- No previous topic.
- Relevant Slides:
-
Traditional Classes of Computer Systems
collapsed:: true- What is a Personal Computer (PC)?
card-last-score:: 5
card-repeats:: 2
card-next-schedule:: 2022-09-23T18:28:00.836Z
card-last-interval:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.7
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-09-19T18:28:00.836Z
- A Personal Computer is a computer designed for use by an individual, usually incorporating a graphics display, a keyboard, and a mouse.
- What is a Server? #card
card-last-interval:: 41.44
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.18
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-22T21:33:20.708Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-11T11:33:20.709Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A server is a computer used for running larger programs for multiple users, often simultaneously, and typically accessed only via a network.
- What is a Supercomputer?
card-last-interval:: 11.2
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.8
card-next-schedule:: 2022-10-14T15:37:52.646Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-03T11:37:52.647Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A supercomputer is a member of a class of computers with the highest performance (and cost). They are configured as servers and typically cost tens to hundreds of millions of dollars.
- What is an Embedded Computer? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:45:01.338Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:45:01.338Z
card-last-score:: 5
- An embedded computer is a computer inside another device, used for running one predetermined application or collection of software.
- What are Personal Mobile Devices?
card-last-interval:: 11.2
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.8
card-next-schedule:: 2022-10-12T21:31:08.211Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-01T17:31:08.211Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Personal Mobile Devices are small, wireless devices that connect to the internet.
- They rely on batteries for power, and software is installed by downloading apps.
- Conventional examples include smartphones and tablets.
- What is Cloud Computing? #card
card-last-interval:: 29.26
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T22:41:13.223Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:41:13.223Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Cloud Computing refers to large collections of servers that provide services over the internet.
- Some providers rent dynamically varying number of servers as a utility.
- What is Software as a Service? #card
card-last-interval:: 29.26
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T22:47:42.790Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:47:42.790Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Software as a Service delivers software & data as a service over the internet, usually via a thing program, such as a browser.
- Examples include web search & email.
- What is a Personal Computer (PC)?
card-last-score:: 5
card-repeats:: 2
card-next-schedule:: 2022-09-23T18:28:00.836Z
card-last-interval:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.7
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-09-19T18:28:00.836Z
-
Computer Systems
 {:height 410, :width 414}
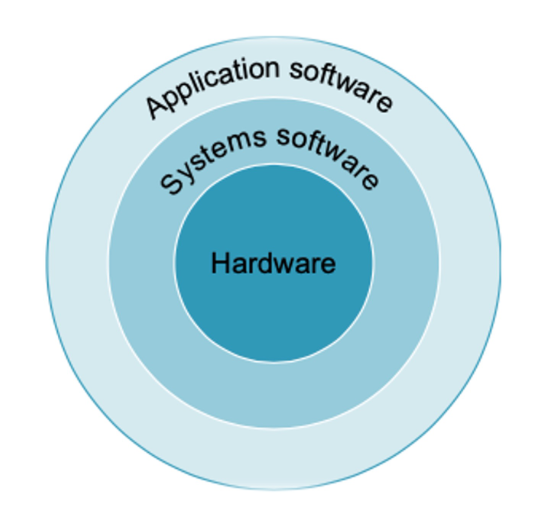
{:height 410, :width 414}- What is Application Software? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:45:07.567Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:45:07.567Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Application Software consists of user-installed applications & programs.
- Application Software provides services to the user that are commonly useful.
- What is the purpose of the Operating System? #card
card-last-interval:: 49.07
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.28
card-next-schedule:: 2023-01-02T21:21:34.885Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:21:34.886Z
card-last-score:: 3
- The Operating System interfaces between a user's program and the hardware, provides a variety of services, and performs supervisory functions.
- What is the purpose of the Hardware?
- The Hardware performs the tasks.
-
Seven Great Ideas in Computer Organisation
-
1. Use Abstraction to Simplify Design #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64 card-repeats:: 4 card-ease-factor:: 2.9 card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T10:59:55.160Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T19:59:55.163Z card-last-score:: 5- A major productivity technique for hardware & software is to use abstractions to characterise the design at different levels of representation
- Lower-level details are hidden to offer a simpler model at higher levels.
-
2. Make the Common Case Fast #card
card-last-interval:: 29.26 card-repeats:: 4 card-ease-factor:: 2.66 card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T22:41:18.214Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:41:18.214Z card-last-score:: 5- Making the common case fast will tend to enhance performance better than optimising the rare case.
- The common case is often simpler than the rare case, and hence is usually easier to enhance.
-
3. Performance via Parallelism #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3 card-repeats:: 4 card-ease-factor:: 2.66 card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-17T15:35:06.365Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-20T08:35:06.365Z card-last-score:: 5- Involves speeding up performance by using designs that compute operations in parallel.
-
4. Performance via Pipelining #card
card-last-interval:: 27.13 card-repeats:: 4 card-ease-factor:: 2.56 card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-11T19:29:57.240Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:29:57.241Z card-last-score:: 3- Performance via Pipelining is a particular pattern of parallelism that is so prevalent in computer architecture that it merits its own name.
-
5. Performance via Prediction #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64 card-repeats:: 4 card-ease-factor:: 2.9 card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-15T02:32:12.139Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-11T11:32:12.139Z card-last-score:: 5- In some cases, it can be ^^faster on average to guess and start working^^ that to wait until you know for sure (assuming that the mechanism to recover from a misprediction is not too expensive, and your prediction is relatively accurate).
-
6. Hierarchy of Memories #card
card-last-interval:: 29.26 card-repeats:: 4 card-ease-factor:: 2.66 card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T22:42:13.815Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:42:13.816Z card-last-score:: 5- Computer Architects have found that they can address conflicting demands with a hierarchy of memories.
- The ^^fastest, smallest, & most expensive memory per bit^^ is at the top of the hierarchy.
- The ^^slowest, largest, & cheapest per bit^^ is at the bottom of the hierarchy.
- Computer Architects have found that they can address conflicting demands with a hierarchy of memories.
-
7. Dependability via Redundancy #card
card-last-interval:: 29.26 card-repeats:: 4 card-ease-factor:: 2.66 card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T22:42:16.723Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:42:16.723Z card-last-score:: 5- Since any physical device can fail, we make systems dependable by including ^^redundant components^^ that can take over when a failure occurs and help detect failures.
-
-
Hardware Organisation
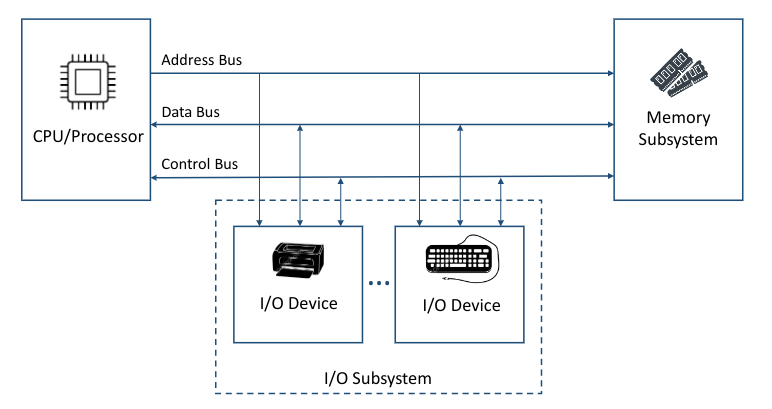
- What does basic computer organisation look like? #card card-last-interval:: 33.64 card-repeats:: 4 card-ease-factor:: 2.9 card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-22T23:24:24.522Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-20T08:24:24.523Z card-last-score:: 5
- What is an integrated circuit?
card-last-interval:: 31.36
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.8
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-04T20:17:29.178Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-04T12:17:29.178Z
card-last-score:: 5
collapsed:: true
- An integrated circuit, also called a chip, is a device combining dozens to millions of transistors.
-
The CPU
- What is a CPU? #card
card-last-interval:: 29.26
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T22:47:19.225Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:47:19.226Z
card-last-score:: 5
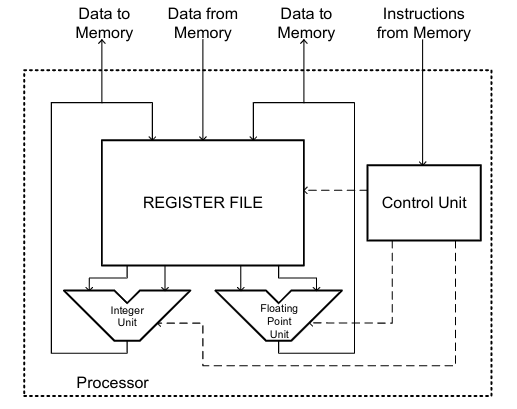
- The Central Processing Unit (CPU), also called the processor, is the ^^active part of the computer^^, which contains the datapath & control, and which adds numbers, tests numbers, signals I/O devices to activate, and so on.
- The CPU is ^^responsible for executing programs.^^
- What are the steps that the CPU takes to process programs? #card
card-last-interval:: 64.01
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.52
card-next-schedule:: 2023-01-17T20:21:39.209Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:21:39.209Z
card-last-score:: 5
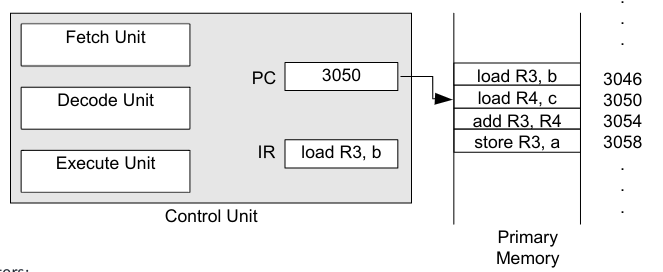
- 1. Fetch: Retrieve an instruction from ^^program memory.^^
- 2. Decode: Break down the instruction into parts that have significance to specific sections of the CPU.
- 3. Execute: Various portions of the CPU are connected to perform the desired operation.
- 4. Write Back: Simply "writes back" the results of the execute step ^^if necessary.^^
-
CPU Organisation
- What does the organisation of the CPU look like? #card card-last-interval:: -1 card-repeats:: 1 card-ease-factor:: 1.94 card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-15T00:00:00.000Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:12:31.318Z card-last-score:: 1
-
Control Unit
- What does the Control Unit do? #card
card-last-interval:: -1
card-repeats:: 1
card-ease-factor:: 2.56
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-15T00:00:00.000Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:48:27.996Z
card-last-score:: 1
- The Control Unit ^^controls the execution^^ of the instructions stored in main memory.
- It ^^retrieves & executes^^ them.
- The Control Unit ^^controls the execution^^ of the instructions stored in main memory.
- What is the architecture of the control unit? #card card-last-interval:: -1 card-repeats:: 1 card-ease-factor:: 2.08 card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-15T00:00:00.000Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:18:27.653Z card-last-score:: 1
- What does the Control Unit do? #card
card-last-interval:: -1
card-repeats:: 1
card-ease-factor:: 2.56
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-15T00:00:00.000Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:48:27.996Z
card-last-score:: 1
- What is a CPU? #card
card-last-interval:: 29.26
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T22:47:19.225Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:47:19.226Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
The Memory Subsystem
collapsed:: true- How is the memory divided into storage locations? #card
card-last-interval:: 29.26
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T22:41:41.185Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:41:41.185Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Memory is divided into a set of storage location which can hold data.
- Locations are numbered.
- Addresses are used to tell the memory which location the processor wants to access.
- Memory is divided into a set of storage location which can hold data.
- What are the two hierarchies of memory? #card
card-last-interval:: 10.97
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.56
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-25T15:41:01.018Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:41:01.018Z
card-last-score:: 5
- 1. Nonvolatile / ROM (Read Only Memory): Read only memory.
- Used to store the BIOS and / or a bootstrap or bootloader program.
- 2. Volatile / RAM (Random Access Memory): Read / Write memory.
- Also called Primary Memory.
- Used to hold the programs, operating system, and data required by the computer.
- 1. Nonvolatile / ROM (Read Only Memory): Read only memory.
-
Primary Memory
- How is primary memory connected to the CPU? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-15T02:38:12.876Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-11T11:38:12.876Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Primary Memory is directly connected to the Central Processing Unit of the computer.
- It must be present for the CPU to function correctly.
- Primary Memory is directly connected to the Central Processing Unit of the computer.
- What are the three types of Primary Storage? #card
card-last-interval:: -1
card-repeats:: 1
card-ease-factor:: 2.08
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-15T00:00:00.000Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:35:22.469Z
card-last-score:: 1
- 1. Processor Register:
- Contains information that the CPU needs to carry out the current instruction.
- 2. Cache Memory:
- A special type of internal memory used by many CPUs to increase their throughput.
- 3. Main Memory:
- Contains the programs that are currently being run and the data that the programs are operating on.
- 1. Processor Register:
- How is primary memory connected to the CPU? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-15T02:38:12.876Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-11T11:38:12.876Z
card-last-score:: 5
- What is the address width? #card
card-last-interval:: 47.41
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.28
card-next-schedule:: 2023-01-07T22:09:51.569Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-21T13:09:51.569Z
card-last-score:: 3
- The address width is the number of bits used to represent an address in memory.
- The width limits the amount of memory that a computer can access.
- Most computers use a 64 bit address, which means that the maximum number of locations is 2^{64} \approx 16 billion gigabytes.
- What operations does the memory subsystem support? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-12T23:44:58.031Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:44:58.031Z
card-last-score:: 3
- The memory subsystem supports two operations:
- Load (or read) + the address of the data location to be read.
- Store (or write) + the address of the location & the data to be written.
- The memory subsystem supports two operations:
- How many bytes may the memory system read or write at a time? #card
card-last-interval:: 29.26
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T22:41:30.763Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:41:30.764Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Read & Write operations ^^operate at the width of the system's data bus^^, usually 32 bit or 64 bit.
- How is a section of memory addressed? #card
card-last-interval:: -1
card-repeats:: 1
card-ease-factor:: 2.8
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-15T00:00:00.000Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:43:58.787Z
card-last-score:: 1
- The address ^^contains only the address of the lowest byte^^, and a number of bytes to be read is specified, e.g., 4 bytes.
-
Memory Alignment & Words of Data
- When the computer's word size is 4 bytes, the data to be read should be at a memory address which is ^^some multiple of four.^^
- When this is not the case, e.g., the data starts at address 14 instead of 16, then the computer has to read two or more 4 byte chunks and do some calculation before the requested data has been read, or it may generate ^^an alignment fault.^^
- Even though the previous data structure end is at, for example, address 13, the next data structure should start at address 16. Two padding bytes are inserted between the two data structures at addresses 14 & 15 to align the next data structure at address 16.
- How is the memory divided into storage locations? #card
card-last-interval:: 29.26
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T22:41:41.185Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:41:41.185Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
The I/O Subsystem
- What are input devices? #card
collapsed:: true
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:38:20.415Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:38:20.415Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Anything that feeds data into the computer.
- What are output devices? #card
collapsed:: true
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:38:27.684Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:38:27.684Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Display / transmit information back to the user.
- What does the I/O Subsystem contain? #card
collapsed:: true
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:38:17.443Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:38:17.443Z
card-last-score:: 5
- The I/O Subsystem contains the devices that the computer uses to communicate with the outside world and to store data.
- How do I/O devices communicate with the processor? #card
collapsed:: true
card-last-interval:: 10.24
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-24T21:49:01.266Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:49:01.266Z
card-last-score:: 3
- I/O devices usually communicate with the processor using the I/O Bus.
- PCs use the PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) bus for their I/O bus.
- The Operating System needs a device driver to access a given I/O device.
- What is a device driver? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:43:53.294Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:43:53.295Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A device driver is a program that allows the OS to control an I/O device.
- What is a device driver? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:43:53.294Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:43:53.295Z
card-last-score:: 5
- I/O devices usually communicate with the processor using the I/O Bus.
- What are input devices? #card
collapsed:: true
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:38:20.415Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:38:20.415Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
I/O Read / Write Operations
- The I/O read & write operations are similar to the memory read & write operations.
- How does the processor address I/O devices? #card
card-last-interval:: 12.96
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 1.8
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-27T19:18:57.241Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:18:57.241Z
card-last-score:: 3
- A processor may use:
- Memory-Mapped I/O: when the address of the I/O device is in the direct memory space, and the ^^sequences to read/write data in the device are the same as the memory read/write sequences.^^
- Isolated I/O: similar process to Memory-Mapped I/O, but the processor has a ^^second set of control signals to distinguish between a memory access and am I/O access.^^
- What is IO/M? #card
card-last-interval:: 19.01
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.18
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-03T20:02:23.177Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:02:23.177Z
card-last-score:: 3
- IO/M is a status signal in Isolated I/O that denotes whether the read/write operation pertains to the memory or to the I/O subsystem.
- When the signal is low (IO/M = 0), i.e., IO/M is
true, it denotes memory-related operations. - When the signal is high, (IO/M = 1), i.e., IO/M is
false, it denotes an I/O operation.
- When the signal is low (IO/M = 0), i.e., IO/M is
- IO/M is a status signal in Isolated I/O that denotes whether the read/write operation pertains to the memory or to the I/O subsystem.
- A processor may use:
-
Programs
- What are programs? #card
card-last-interval:: 23.43
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-08T02:39:39.879Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:39:39.879Z
card-last-score:: 3
- Programs are ^^sequences of instructions^^ that tell the computer what to do.
- To the computer, a program is made out of a ^^sequence of numbers that represent individual operations.^^
- These operations are known as machine instructions or just instructions.
- A set of instructions that a processor can execute is known as an instruction set.
-
Program Development Tools
collapsed:: true- What is a high-level programming language? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:43:16.217Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:43:16.218Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A high-level programming language is a ^^portable language^^ such as C that is ^^composed of words & algebraic notation^^ that can be translated by a compiler into assembly language.
- What is a compiler? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:38:38.718Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:38:38.719Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A compiler is a program that translates statements in a given high-level language into assembly language statements.
- What is an assembler? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:43:18.677Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:43:18.677Z
card-last-score:: 5
- An assembler is a program that translates symbolic, assembly language versions of instructions into the ^^binary version.^^
- What is Assembly Language? #card
card-last-interval:: 108
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 3
card-next-schedule:: 2023-03-02T20:22:13.316Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:22:13.317Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Assembly Language is a ^^symbolic representation^^ of machine instructions.
- What is Machine Language? #card
card-last-interval:: 19.01
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.18
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-03T20:02:29.114Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:02:29.114Z
card-last-score:: 3
- Machine Language is a ^^binary representation^^ of machine instructions.
- What is an instruction? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-12T23:49:56.176Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:49:56.176Z
card-last-score:: 3
- An instruction is a command that the computer hardware understands & obeys.
- What is a high-level programming language? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:43:16.217Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:43:16.218Z
card-last-score:: 5
- What are programs? #card
card-last-interval:: 23.43
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-08T02:39:39.879Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:39:39.879Z
card-last-score:: 3
-
Operating Systems
- What is an Operating System? #card
card-last-interval:: 9.68
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-24T08:36:28.473Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:36:28.474Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Possible definition: a program that runs on the computer that ^^knows about all the hardware^^ and usually ^^runs in privileged mode^^, having ^^access to physical resources that user programs can't control^^, and has the ^^ability to start & stop user programs.^^
- The OS is responsible for managing the physical resources of complex systems, such as PCs, workstations, mainframe computers, etc.
- It is also responsible for ^^loading & executing programs^^ and ^^interfacing with the users.^^
- Usually, there is no operating system for small embedded systems.
- Computers designed for one specific task.
-
Multiprogramming
- What is Multiprogramming? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-17T15:33:42.952Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-20T08:33:42.952Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Multiprogramming is a technique that allows the system to ^^present the illusion that multiple programs are running on the computer simultaneously.^^
- Many multiprogrammed computers are multiuser.
- They allow multiple users to be logged in at a time.
- How is multiprogramming achieved? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-12T23:46:17.294Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:46:17.294Z
card-last-score:: 3
- Multiprogramming is achieved by ^^switching rapidly between programs.^^
- How does the processor decide which process to execute next? #card
card-last-interval:: 23.43
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-08T02:44:23.286Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:44:23.287Z
card-last-score:: 5
- FCFS - First Come, First Served: processes are moved to the CPU in the order in which they arrive.
- SJN - Shortest Job Next: looks at all processes in the ready state and dispatches the one with the smallest service time.
- Round Robin: distributes the processing time equitably among all ready processes.
-
Context Switching
- What is a Context Switch? #card
card-last-interval:: 64.01
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.52
card-next-schedule:: 2023-01-24T13:09:58.962Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-21T13:09:58.962Z
card-last-score:: 5
- When a program timeslice ends, the OS stops it, removes it, and gives another program control over the processor.
- This is a context switch.
- When a program timeslice ends, the OS stops it, removes it, and gives another program control over the processor.
- How does the OS go about a Context Switch? #card
card-last-interval:: 15.05
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 1.94
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-29T17:40:02.859Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:40:02.859Z
card-last-score:: 3
- copies the current program register file into memory
- restores the contents of the next program's register file into the processor
- starts executing the next program
- From the program point of view, ^^no program can tell that a context switch has been performed.^^
- What is a Context Switch? #card
card-last-interval:: 64.01
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.52
card-next-schedule:: 2023-01-24T13:09:58.962Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-21T13:09:58.962Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Protection
- Three rules of Protection in multiprogrammed computers: #card
card-last-interval:: 29.21
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 1.94
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-17T00:35:54.999Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-17T19:35:55.000Z
card-last-score:: 3
-
- The result of any program running on the multiprogram computer ^^must be the same as if the program was the only program running on the computer.^^
-
- Programs ^^must not be able to access other programs' data^^ and must be confident that their data will not be modified by other programs (for security and privacy).
-
- Programs ^^must not interfere with other programs' use of I/O devices.^^
-
- How is protection achieved? #card
card-last-interval:: 15.05
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 1.94
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-29T21:01:17.902Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:01:17.902Z
card-last-score:: 3
- Protection is achieved by the ^^operating system having full control over the resources of the system (processor, memory, and I/O devices)^^ through:
- Privileged Mode: the operating system is the only one that can control the physical resources it executes in privileged mode.
- User programs execute in user mode.
- Virtual Memory: each program operates as if it were the only program on the computer, occupying a full set of the address space in its virtual space.
- The OS is translating memory addresses that the program references into physical addresses used by the memory system.
- Privileged Mode: the operating system is the only one that can control the physical resources it executes in privileged mode.
- Protection is achieved by the ^^operating system having full control over the resources of the system (processor, memory, and I/O devices)^^ through:
- Three rules of Protection in multiprogrammed computers: #card
card-last-interval:: 29.21
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 1.94
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-17T00:35:54.999Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-17T19:35:55.000Z
card-last-score:: 3
- What is Multiprogramming? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-17T15:33:42.952Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-20T08:33:42.952Z
card-last-score:: 5
- What is an Operating System? #card
card-last-interval:: 9.68
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-24T08:36:28.473Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:36:28.474Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Next Topic: Programming Models