6.7 KiB
6.7 KiB
- #CT2106 - Object-Oriented Programming
- Previous Topic: OOP Modelling
- Next Topic: Coding Up Inheritance
- Relevant Slides:
-
Object Equality #card
card-last-interval:: 11.2 card-repeats:: 3 card-ease-factor:: 2.8 card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-26T00:11:36.263Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:11:36.264Z card-last-score:: 5- When you use
==with reference variables, you are checking if the variables point to the same object.- So, using
==on strings will only return true if the Strings are references to the same object. It will return to false even if the strings contain the same data. - The value of a string variable is the memory location where its String object is stored.
- So, using
- When checking for equality between objects, you must use the
equalsmethod.- The
equalsmethod is an instance method that ^^all objects of built-in classes have.^^- However, for any class that you define, you will have to write your own equals method.
- All equals methods must have the following method signature:
-
public boolean equals(Object object)
-
- All equals methods must have the following method signature:
- However, for any class that you define, you will have to write your own equals method.
- Its specific purpose is to define equality between objects.
- It returns a boolean value.
- It is commutative.
str1.equals(str4)returns the same value asstr4.equals(str1).
- Example:
-
String str1 = "Java"; String str2 = "Ja"; String str3 = "va"; String str4 = str2 + str3; str1.equals(str4) ? System.out.println("true") : System.out.println("false");
-
- The
- When you use
-
card-last-interval:: -1 card-repeats:: 1 card-ease-factor:: 2.6 card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-15T00:00:00.000Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:42:22.854Z card-last-score:: 1instanceof#cardinstanceofis an operator that is used to determine if a variable is pointing to an object with a particular type.-
System.out.println(bike2 instanceof Bicycle ? "true" : "false");
-
-
Object
collapsed:: true- What is the type of
Object obj? #card card-last-interval:: 4 card-repeats:: 2 card-ease-factor:: 2.7 card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-18T16:42:30.590Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:42:30.590Z card-last-score:: 5objis a variable whose type isjava.lang.Object.
- What is
java.lang.Object? #card card-last-interval:: 4 card-repeats:: 2 card-ease-factor:: 2.7 card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-18T16:42:35.503Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:42:35.504Z card-last-score:: 5java.lang.Objectis a class that provides the ^^most generic definition^^ of an object in Java.- It is the parent class of every class in Java.
- For example. A
Bicycleobject is aBicycleobject and ajava.lang.Objectobject.
- What is the type of
-
Casting
-
Bicycle bike1 = (Bicycle) myObject; String str1 = (String) obj;- Here, we can cast (convert) a variable from a higher type (
Object), to a lower type (Bicycle).- This is allowed, as
anObjectpoint to a Bicycle object - we can check this usinginstanceof. objpoints to a String object - we can check this usinginstanceof.
- This is allowed, as
- Here, we can cast (convert) a variable from a higher type (
- Note that the variable type being converted is ^^not the object.^^
-
-
Class Hierarchy
-
Is-a Relationships
- Java organises all its classes in a class hierarchy.
- For example, a car is a type of vehicle, which is a type of object.
- These relationships can be described as "is-a" relationships.
- A car is-a vehicle; a vehicle is-a(n) object.
- We refer the higher-up types as parents and the lower types as children.
- Car is-a child of Vehicle.
- Vehicle is-a parent of Car.
- Object is the parent of Vehicle & Car.
- Java organises all its classes in a class hierarchy.
-
Key Ideas in Class Hierarchy
- The top of the hierarchy represents the ^^most generic attributes & behaviours.^^
- The bottom (sometimes referred to as "leaves") represent the ^^most specific attributes & behaviours.^^
- Each level inherits and customises the attributes & behaviours from the level above it.
java.lang.Objectis the superclass, the parent of all classes in Java.- Every class in Java has the
java.lang.Objectas its superclass (parent). 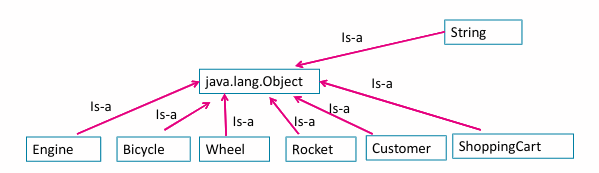
- All the classes shown above inherit (receive) methods from the superclass
java.lang.Object.- What is OOP Inheritance? #card
card-last-interval:: 5.52
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.46
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-20T04:38:03.406Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:38:03.406Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Inheritance is the means by which objects automatically receive features (fields) & behaviours (methods) from their superclass.
- What is OOP Inheritance? #card
card-last-interval:: 5.52
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.46
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-20T04:38:03.406Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:38:03.406Z
card-last-score:: 5
- The methods of this superclass are available to all objects of this Class, even though these methods may not be shown in the Class code.
- For example:
.equals(). -
Generic Methods
- All the methods provided by the
java.lang.Objectare generic.- They only relate to
java.lang.Objectclasses, not the subclasses. - When a subclass inherits these methods, it needs to customise them.
- This is why we had to override
.equals()with our own version for the example Bicycle class.
- This is why we had to override
- They only relate to
- All the methods provided by the
- For example:
- All the classes shown above inherit (receive) methods from the superclass
-
Overriding
- What is overriding? #card
card-last-interval:: 29.99
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.56
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-14T19:04:47.436Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:04:47.437Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Overriding is when you write your own version of a method that you have inherited from a superclass.
- It is creating a specific version of a method inherited from a parent (superclass) class.
- When overriding a method, you must keep every part of the method signature the same - You can only change the code in the method body.
- Its name, its parameter types & order, its access level (e.g., public, protected), and its return type.
- Overriding is when you write your own version of a method that you have inherited from a superclass.
-
Annotation
- It is good practice to annotate your overridden methods using
@Override.- You code will compile & run without it, but it is considered good practice to annotate the methods that are overridden inherited from the superclass.
-
@Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { obj == null ? return false; if (obj instanceof Bicycle) { Bicycle bike = (Bicycle) obj; if (this.speed == bike.getSpeed() && this.gear == bike.getGear()) { return true; } } return false; }
- It is good practice to annotate your overridden methods using
- What is overriding? #card
card-last-interval:: 29.99
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.56
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-14T19:04:47.436Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:04:47.437Z
card-last-score:: 5
-

