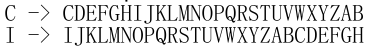15 KiB
15 KiB
- #CT255 - Next Generation Technologies II
- Previous Topic: GDPR
- Next Topic: Human Security & Passwords
- Relevant Slides:
id:: 63265db7-1d41-44f7-b4cf-0bab377a7c1c
-
SQL Injections
- What is an SQL Injection? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-09T18:33:16.312Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-11T11:33:16.312Z
card-last-score:: 5
- An SQL Injection is a code injection technique used to attack data-driven applications, in which malicious SQL statements are inserted for execution.
- It is a way of exploiting user input & SQL statements to compromise the database & retrieve sensitive data.
- What is an SQL Injection? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-09T18:33:16.312Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-11T11:33:16.312Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Basic Terminology
- What is Cryptography? #card
card-last-interval:: 108
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 3
card-next-schedule:: 2023-03-06T18:36:41.369Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-18T18:36:41.370Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Cryptography is the art of encompassing the principles & methods of transforming an intelligible message into one that is unintelligible, and then retransforming that message back into its original form.
- What is Plaintext?
card-last-score:: 5
card-repeats:: 3
card-next-schedule:: 2022-10-17T21:24:55.999Z
card-last-interval:: 11.2
card-ease-factor:: 2.8
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-06T17:24:55.999Z
- Plaintext is the ^^original, intelligible message.^^
- What is Ciphertext?
card-last-interval:: 11.2
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.8
card-next-schedule:: 2022-10-18T14:39:00.206Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-07T10:39:00.207Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Ciphertext is the encrypted messsage.
- What is a Cipher? #card
card-last-interval:: 11
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-25T16:46:20.520Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:46:20.520Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A Cipher is an algorithm for transforming an intelligible message into one that is unintelligible.
- What is a Key? #card
card-last-interval:: 9.68
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-24T08:37:27.630Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:37:27.630Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A Key is some critical information used by the cipher, known only to the sender & receiver, selected from a keyspace (the set of all possible keys).
- What does Encipher mean?
card-last-score:: 5
card-repeats:: 3
card-next-schedule:: 2022-10-17T21:14:43.789Z
card-last-interval:: 11.2
card-ease-factor:: 2.8
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-06T17:14:43.790Z
- Enciphering is the process of converting plaintext into ciphertext using a cipher & a key.
- What does Decipher mean?
card-last-interval:: 4
card-repeats:: 2
card-ease-factor:: 2.7
card-next-schedule:: 2022-10-04T12:09:14.829Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-09-30T12:09:14.829Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Deciphering is the process of converting ciphertext back into plaintext using a cipher & a key.
- What is Encryption? #card
card-last-score:: 5
card-repeats:: 4
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-08T06:02:35.168Z
card-last-interval:: 23.43
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:02:35.168Z
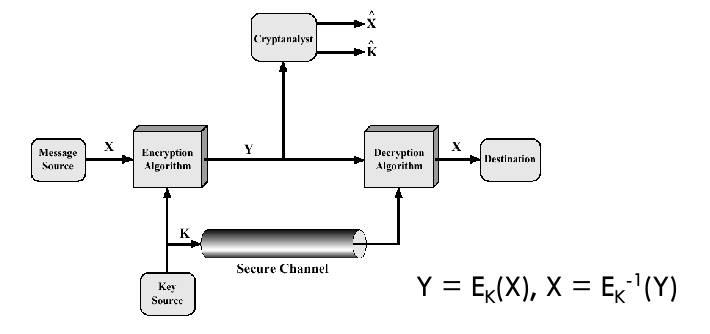
- Encryption is some mathematical function
E_K()mapping plaintextPto ciphertextCusing the specified keyK. -
E_K(P) = C
- Encryption is some mathematical function
- What is Decryption? #card
card-last-interval:: 9.68
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-24T08:49:17.364Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:49:17.365Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Decryption is some mathematical function
{E_K}^{-1}()mapping the ciphertextCto plaintextPusing the specified keyK. -
P={E_K}^{-1}(C)
- Decryption is some mathematical function
- What is Cryptanalysis? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-16T15:43:11.780Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-19T08:43:11.781Z
card-last-score:: 3
- Cryptanalysis is the study of principles & methods of transforming an unintelligible message into an intelligible message without knowledge of the key.
- What is Cryptology?
card-last-interval:: 9.28
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-10-16T16:40:03.776Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-07T10:40:03.777Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Cryptology is the field encompassing both cryptography & cryptanalysis.
- What is Cryptography? #card
card-last-interval:: 108
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 3
card-next-schedule:: 2023-03-06T18:36:41.369Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-18T18:36:41.370Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Model of Conventional Cryptosystem
-
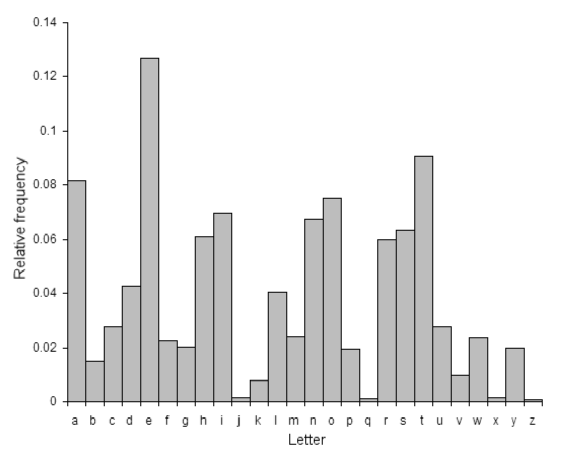
Cryptanalysis via Letter Frequency Distribution
- Human languages are redundant - letters are not equally commonly used.
- In the English language:
-
C Program for Frequency Analysis of single Characters
-
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <ctype.h> int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { FILE* fp; int data[26]; char c; memset(data, 0, siezof(data)); if (argc != 2) { return(-1); } if (fp = fopen(argv[1], "r" == NULL)) { return(-2); } while(!feof(fp)) { c = toupper(fgetc(fp)); if ((c >= 'A') && (c <= 'Z')) { data[c-65]++; } } for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) { printf("%c:%i\n", i+65, data[i]); } fclose(fp); return(0); }
-
-
Known Plaintext Attacks (KPA)
- What is a Known Plaintext Attack (KPA)? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T03:02:00.417Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:02:00.417Z
card-last-score:: 5
- The Known Plaintext Attack (KPA) is an attack model for cryptanalysis where the attacker has access to both:
- some of, or all of, the plaintext (called a crib)
- the ciphertext
- The Known Plaintext Attack (KPA) is an attack model for cryptanalysis where the attacker has access to both:
- What is a Known Plaintext Attack (KPA)? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T03:02:00.417Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:02:00.417Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Caesar Cipher
- What is a Caesar Cipher? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T11:04:27.582Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:04:27.582Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A Caesar Cipher involves using an offset alphabet to encrypt a message.
- We can use any shift from 1 to 25 to replace each plaintext letter with a letter a fixed distance away.
- The key letter represents the start of this offset alphabet.
- For example, a key letter of F means that A -> F, B -> G, and so on.
- What is a Caesar Cipher? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T11:04:27.582Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:04:27.582Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Playfair Cipher
- Not even the large number of keys in a monoalphabetic cipher provides security.
- What is a monoalphabetic cipher? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T03:02:37.487Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:02:37.488Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A monoalphabetic cipher is any cipher in which the letters of the plaintext are mapped to ciphertext letters based on a single alphabetic key.
- What is a monoalphabetic cipher? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T03:02:37.487Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:02:37.488Z
card-last-score:: 5
- One approach to improving security over monoalphabetic ciphers is to to encrypt ^^multiple letters.^^
- The Playfair Cipher is one example of such an approach.
- The algorithm was invented by Charles Wheatstone in 1854, but named after his friend Baron Playfair.
-
How does the Playfair Cipher work?
card-last-score:: 5 card-repeats:: 2 card-next-schedule:: 2022-10-08T00:33:19.557Z card-last-interval:: 3.51 card-ease-factor:: 2.6 card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-04T12:33:19.558Z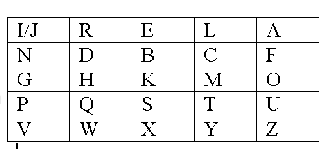
-
- Create a 5x5 grid of letters; insert the keyword as shown, with each letter only considered once; fill the grid with the remaining letters in alphabetic order.
-
- The letters are then encrypted in pairs.
-
- Repeats have an "X" inserted.
- BALLOON -> BA LX LO ON
-
- Letters that fall in the same row are replaced with the letter on the right.
- OK -> GM
-
- Letters in the same column are replaced with the letter below.
- FO -> OU
-
- Otherwise, each letter gets replaced by the letter in its row but in the other letters column.
- QM -> TH
-
Security of the Playfair Cipher
- The security is much improved over simple monoalphabetic ciphers, as the Playfair Cipher has
26^2 = 676combinations.- This requires a 676 entry frequency table to analyse (as compared to a 26 entry frequency table for a monoalphabetic cipher) and correspondingly, more ciphertext.
- However, the Playfair Cipher can be cracked through frequency analysis of letter pairs, given a few hundred letters.
- The security is much improved over simple monoalphabetic ciphers, as the Playfair Cipher has
- Not even the large number of keys in a monoalphabetic cipher provides security.
-
Vigenère Cipher
- Blaise de Vigenère is generally credited as the inventor of the Polyalphabetic Substitution Cipher.
- What is a Polyalphabetic Substitution Cipher? #card
card-last-interval:: 11.2
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.8
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-25T20:35:52.727Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:35:52.727Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A Polyalphabetic Substitution Cipher uses multiple substitution alphabets, as opposed to a monoalphabetic cipher which uses a single alphabetic key.
- What is a Polyalphabetic Substitution Cipher? #card
card-last-interval:: 11.2
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.8
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-25T20:35:52.727Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:35:52.727Z
card-last-score:: 5
- The Vigenère Cipher improves security by using many monoalphabetic substitution alphabets, so each letter can be replaced by many others.
- You use a key to select which alphabet is used for each letter of the message.
- The
i^{th}letter of the key specifies thei^{th}alphabet to use. - Use each alphabet in turn.
- Repeat from the start after the end of the key is reached.
- The
-
Vigenère Steps
-
How to crack the Vigenère Cipher
-
- Search the ciphertext for repeated strings of letters - the longer the string, the better.
-
- For each occurrence of a repeated string, count how many letters are between the first letters in the string, and add one.
-
- Factorise that number.
-
- Repeat this process with each repeated string you find and make a table of common factors. The most common factor,
nis most likely the length of the keyword used to encipher the ciphertext.
- Repeat this process with each repeated string you find and make a table of common factors. The most common factor,
-
- Do a frequency count on the ciphertext, on every
n^{th}letter. You should end up withndifferent frequency counts.
- Do a frequency count on the ciphertext, on every
-
- Compare these counts to standard frequency tables to figure out how much each letter was shifted by.
-
- Undo the shifts and read the message.
-
- Blaise de Vigenère is generally credited as the inventor of the Polyalphabetic Substitution Cipher.
-
Enigma (Rotor Ciphers)
-
Rotor Ciphers
- The mechanisation / automation of encryption.
- An $\text{N}$-stage polyalphabetic algorithm modulo 26.
26^Nsteps before a repetition, whereNis the number of cylinders.- The Enigma machine had 5 cylinders, so:
-
26^{N=5}=11,881,376 \text{ steps}
-
- The Enigma machine had 5 cylinders, so:
-
Breaking Enigma using Cribs
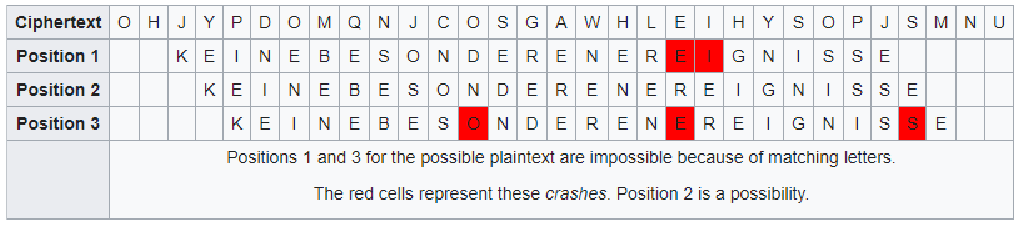
- The starting point for breaking Enigma was based on the following:
- Plaintext messages were likely to contain certain phrases.
- Weather reports contained the term "WETTER VORHERSAGE".
- Military units often sent messages containing "KEINE BESONDEREN EREIGNISSE" ("nothing to report").
- A plaintext letter was never mapped onto the same ciphertext letter.
- Plaintext messages were likely to contain certain phrases.
- While the cryptanalysts in Bletchely Park did not know exactly where these cribs were placed in an intercepted message, they could exclude certain positions.
- The starting point for breaking Enigma was based on the following:
-
-
Transposition Ciphers
- What are Transposition Ciphers? #card
card-last-interval:: 21.53
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-06T08:01:53.099Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:01:53.100Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Transposition or Permutation Ciphers hide the message by rearranging the letter order ^^without altering the actual letters used.^^
- This can be recognised since the ciphertext has the same frequency distribution as the original text.
-
Rail Fence Cipher
id:: 6344093b-2f4f-4c58-95e4-39a8b30d16c3 -
Row Transposition Cipher
- What are Row Transposition Ciphers? #card
card-last-interval:: 86.42
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2023-02-09T06:21:27.811Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:21:27.811Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Row Transposition Ciphers are a more complex kind of transposition cipher than ((6344093b-2f4f-4c58-95e4-39a8b30d16c3))s.
- Plaintext letters are written out in rows over a specified number of columns.
- The columns are then re-ordered according to some key before reading off the columns

- What are Row Transposition Ciphers? #card
card-last-interval:: 86.42
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2023-02-09T06:21:27.811Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:21:27.811Z
card-last-score:: 5
- What are Transposition Ciphers? #card
card-last-interval:: 21.53
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-06T08:01:53.099Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:01:53.100Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Product Ciphers
- Ciphers using just substitutions or transpositions are not secure because of language characteristics.
- Consider using several ciphers in succession to make it harder to crack:
- Two substitutions make a more complex substitution.
- Two transpositions make a more complex transposition.
- However, a substitution followed by a transposition makes a much harder cipher.
-
Steganography
- What is Steganography? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-21T10:35:36.194Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-17T19:35:36.195Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Steganography is an alternative to encryption that hides the existence of the message.
- For example:
- Using only a subset of letters / words in a message marked in some way.
- Using invisible ink.
- Hiding in LSB in graphic image or sound file.
- The drawback of steganography is that it's not very economical in terms of overheads to hide a message.
- What is Steganography? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-21T10:35:36.194Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-17T19:35:36.195Z
card-last-score:: 5