7.1 KiB
7.1 KiB
- #CT2106 - Object-Oriented Programming
- Previous Topic: Introduction to Java
- Next Topic: More Java Code
- Relevant Slides:
- What is the structure of a class? #card
card-last-interval:: 21.53
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-01T00:46:31.046Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-09T12:46:31.046Z
card-last-score:: 3
- Every class has the following structure:
-
public class ClassName { Fields Constructors Methods }
-
- Every class has the following structure:
-
Fields
- What are Fields? #card
card-last-interval:: 86.42
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2023-02-09T06:22:08.706Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:22:08.706Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Fields, also known as instance variables, store values for an object.
- Fields define the state of an object.
- In BlueJ, use Inspect to view the state.
- Some values change frequently, others rarely, or not at all.
- What are Fields? #card
card-last-interval:: 86.42
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2023-02-09T06:22:08.706Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:22:08.706Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Encapsulation
- What is Encapsulation? #card
card-last-interval:: 9.68
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-24T08:35:40.664Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:35:40.665Z
card-last-score:: 5
- In encapsulation, the ^^variables of a class will be hidden from other classes^^ and can only be accessed through the methods of their current class.
- This is also known as data hiding.
- Why use encapsulation? #card
card-last-interval:: 22.66
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.38
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-07T11:20:26.959Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:20:26.960Z
card-last-score:: 5
- In OOP, ^^each object is responsible for its own data.^^
- This allows an object to have greater control over which data is available to be viewed externally, and how external objects can mutate the object's state.
- In OOP, ^^each object is responsible for its own data.^^
-
Encapsulation Type: Private
- What is the effect of making a field private? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-17T15:33:20.443Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-20T08:33:20.443Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Making a field private encapsulates their values inside their object.
- No external class or object can access a private field.
- What is the effect of making a field private? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-17T15:33:20.443Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-20T08:33:20.443Z
card-last-score:: 5
- What is Encapsulation? #card
card-last-interval:: 9.68
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-24T08:35:40.664Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:35:40.665Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Constructors
- What are constructors? #card
card-last-interval:: 25.4
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-10T01:49:12.088Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:49:12.088Z
card-last-score:: 3
- Constructors:
- Initialise an object.
- Have the same name as their class.
- Have a close association with the fields:
- They contain the initial values stored in the fields.
- They contain the parameter values often used for these.
- Constructors:
- What is the point of the keyword
this? #card card-last-score:: 5 card-repeats:: 4 card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:50:05.102Z card-last-interval:: 33.64 card-ease-factor:: 2.9 card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:50:05.103Z- The
thiskeyword refers to the current object in a method or constructor. - The most common use of
thisis to distinguish between class attributes & parameters of the same name. - If the input parameter variables in your constructor have the same name as your fields, you must use the
thiskeyword to distinguish between the two. this= "belonging to this object".- E.g.,
-
public Bicycle(int speed, int gear, int cadence) { this.speed = speed; this.gear = gear; this.cadence = cadence; }
-
- The
- What are constructors? #card
card-last-interval:: 25.4
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-10T01:49:12.088Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:49:12.088Z
card-last-score:: 3
-
Methods
- What are methods? #card
card-last-score:: 5
card-repeats:: 5
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T19:12:15.540Z
card-last-interval:: 33.96
card-ease-factor:: 2.04
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:12:15.540Z
- Methods implement the behaviour of an object.
- They have a consistent structure comprised of a header and a body.
-
Accessor Methods
- What are accessor methods? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-09T18:39:30.677Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-11T11:39:30.678Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Accessor methods provide information about the state of an object.
- An accessor method always returns a type that is not
void. - An accessor method returns a value (result) of the type given in the header.
- The method will contain a return statement to return the value.
- What are accessor methods? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-09T18:39:30.677Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-11T11:39:30.678Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Mutator Methods
- What are mutator methods? #card card-last-interval:: 29.26 card-repeats:: 4 card-ease-factor:: 2.66 card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T22:48:10.566Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:48:10.566Z card-last-score:: 5
-
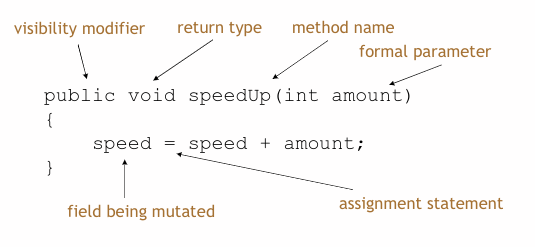
Mutator Methods: Set
- Each field may have a dedicated set mutator method.
- These have a simple, distinctive form:
- void return type
- method name related to the field name
- a single formal parameter, with the same type as the type of the field
- a single assignment statement
- A typical "set" method:
-
public void setGear (int number) { gear = number; }
-
-
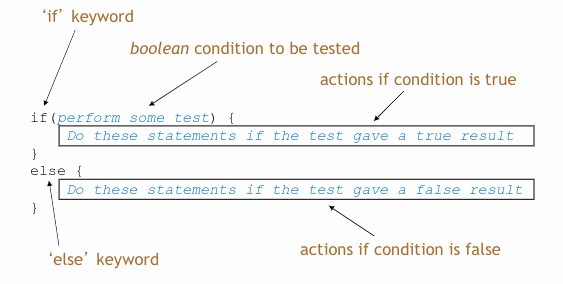
Protector Mutators
- A set method does not always have to assign unconditionally to the field.
- The parameter may be checked for validity and rejected if innappropriate.
- Mutators thereby protect fields.
- Mutators also support encapsulation.
-
Protecting a Field
-
public void setGear (int gearing) { // this conditional statement prevents innapropriate action. // if protects the "gear" field from values that are too large or too small. if (gearing >= 1 && gearing <= 18) { gear = gearing; } else { System.out.println("Exceeds maximum gear ratio. Gear not set"); } }
-
- A set method does not always have to assign unconditionally to the field.
-
Method Structure
- The header:
- The head tells us:
- the visibility of the method to objects of other class.
- whether or not the method returns a result.
- the name of the method.
- whether or not the method takes parameters.
- E.g.,
-
public int getSpeed()
-
- The head tells us:
- The body encloses the method's statements.
- The header:
- What are methods? #card
card-last-score:: 5
card-repeats:: 5
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T19:12:15.540Z
card-last-interval:: 33.96
card-ease-factor:: 2.04
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:12:15.540Z
-
C vs Java
- Unlike C, an OOP program will not have a pool of global variables that each method can access.
- Instead, ^^each object has its own data^^, and other objects rely on the accessor methods of the object to access the data.
-
Conditional Statements