26 KiB
26 KiB
- #CT255 - Next Generation Technologies II
- Previous topic: Introduction to Cybersecurity
- Next Topic: Introduction to Cryptography
- Relevant lecture slides:
-
Motivation
- What are Cyberattacks?
card-last-interval:: 11.2
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.8
card-next-schedule:: 2022-10-12T17:25:05.425Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-01T13:25:05.425Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Cyberattacks are aimed at accessing, changing, or destroying sensitive information, extorting money, or interrupting normal business processes.
- Managing sensitive data may reduce the attack probability, or at least its impact.
- GDPR provides such a regulatory framework
- What are Cyberattacks?
card-last-interval:: 11.2
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.8
card-next-schedule:: 2022-10-12T17:25:05.425Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-01T13:25:05.425Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
General Data Protection Regulation
- What is GDPR? #card
card-last-interval:: 56.69
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2023-01-07T03:40:11.348Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-11T11:40:11.348Z
card-last-score:: 5
- The General Data Protection Regulation is a binding regulation in EU law on data protection in the European Union and the European Economic Area (EEA).
- The primary aim of GDPR is to ^^enhance individuals' control & rights over their personal data and to simplify the regulatory environment for international business.^^
- The regulation contains ^^provisions & requirements related to the processing of personal data of individuals^^ who are located in the EEA, and applies to any enterprise that is processing the personal data of individuals inside the EEA - ^^regardless of its location and the data subjects' citizenship or residence.^^
-
GDPR Overview
- The GDPR sets out several key principles: #card
card-last-interval:: 9.28
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-24T02:20:42.714Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:20:42.715Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Lawfulness
- Fairness & Transparency
- Purpose Limitation
- Data Minimsation
- Accuracy
- Storage Limitation
- Integrity & Confidentiality (Security)
- Accountability
- What is Lawfulness in GDPR? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-17T15:33:16.784Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-20T08:33:16.785Z
card-last-score:: 5
- You must identify ^^valid grounds under the GDPR (known as a "lawful basis")^^ for collecting & using personal data.
- Processing shall be lawful if and to the extent that at least one of the following applies:
- Consensual
- Necessary for the performance of a contract
- Necessary for compliance with a legal obligation
- Necessary to protect the vital interests of the data subject or another person
- Necessary for the performance of a task carried out in public interest
- Necessary for the purpose of legitimate interests
- What is Fairness & Transparency in GDPR? #card
card-last-interval:: 54.82
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2023-01-08T15:19:16.362Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:19:16.362Z
card-last-score:: 5
- You must ^^use personal data in a way that is fair.^^ This means that you must not process the data in a way that is unduly detrimental, unexpected, or misleading to the individuals concerned.
- You must be ^^clear, open, & honest^^ with data subjects from the start about how you will use their personal data.
- At the time personal data is being collected from data subjects, they must be informed via a "Data Protection Notice".
- What is a Data Protection Notice? #card
card-last-interval:: 21.53
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-06T08:01:49.347Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:01:49.348Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A Data Protection Notice entails:
- The identity & contact details of the data controller
- The contact details of the data protection officer
- The purpose of the processing & the legal basis for the processing
- The recipients or categories of recipients of the data
- Details of any transfers out of the EEA, the safeguards in place, and the means by which to obtain a copy of them
- The data retention period or the criteria to determine the data retention period
- The individual's rights (access, rectification & erasure, restriction, complaint)
- A Data Protection Notice entails:
- What is a Data Protection Notice? #card
card-last-interval:: 21.53
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-06T08:01:49.347Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:01:49.348Z
card-last-score:: 5
- What is Purpose Limitation in GDPR? #card
card-last-interval:: 75.28
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2023-01-25T17:31:58.536Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-11T11:31:58.537Z
card-last-score:: 5
- You must be ^^clear about what your purposes for processing^^ are from the start.
- You must ^^record your purposes^^ as part of your documentation obligations and specify them in your privacy information for individuals.
- You ^^can only use the personal data for a new purpose^^ if it is either compatible with your original purpose, you get consent, or you have a clear basis in law.
- What is Data Minimisation in GDPR? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:46:12.936Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:46:12.936Z
card-last-score:: 5
- You must ensure that the personal data that you are processing is:
- adequate - sufficient to properly fulfil your stated purpose
- relevant - has a rational link to that purpose
- limited to what is necessary - you do not hold more than what you need for your stated purpose
- You must ensure that the personal data that you are processing is:
- What is Accuracy in GDPR? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-17T15:35:02.681Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-20T08:35:02.682Z
card-last-score:: 5
- You should take all reasonable steps to ensure that the personal data you hold is ^^not incorrect or misleading^^ as to any matter of fact.
- You may need to ^^keep the personal data updated^^, although this will depend on what you are using it for.
- If you ^^discover that personal data is incorrect or misleading^^, you must take reasonable steps to correct or erase it as soon as possible.
- You must ^^carefully consider any challenges to the accuracy^^ of personal data.
- What is Storage Limitation in GDPR? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:37:31.248Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:37:31.249Z
card-last-score:: 5
- You must not keep personal data for ^^longer than you need it^^.
- You need to think about - and be able to justify - ^^how long you keep personal data^^. This will depend on your purposes for holding the data.
- You need a policy ^^setting standard retention periods^^ wherever possible, to comply with documentation requirements.
- You should also ^^periodically review the data you hold^^, and erase or anonymise it when you no longer need it.
- You must ^^carefully consider any challenges to your retention of data^^.
- Individuals have a right to erasure if you no longer need the data.
- You can ^^keep personal data for longer^^ if you are only keeping it for ^^personal interest archiving, scientific or historical research, or statistical purposes.^^
- What is Accountability & Governance in GDPR? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.93
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.56
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T14:49:09.573Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:49:09.573Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Accountability is one of the data protection principles - it makes you responsible for complying with the GDPR and says that ^^you must be able to demonstrate your compliance.^^
- You need to put in place appropriate technical & organisational measures to meet the requirements of accountability.
- Accountability requires controllers to maintain records of processing activities in order to demonstrate how they comply with the data protection principles, i.e.:
- Inventory of personal data
- Providing assurance of compliance
- Need to document
- Why it is held
- How it is collected
- When it will be deleted
- Who may gain access to it
- What is Integrity & Confidentiality in GDPR? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-16T15:43:04.896Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-19T08:43:04.897Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A key principle of GDPR is that you process personal data ^^securely by means of "appropriate technical & organisational measures"^^ - this is the "security principle".
- Doing this requires you to consider things like ^^risk analysis, organisational policies, and physical + technical measures.^^
- Where appropriate, you should look to use measures such as pseudoanonymisation and encryption.
- Your measures must ensure the ^^"confidentiality, integrity, & availability"^^ of your systems & services and the personal data you process with them.
- The measures must also enable you to ^^restore access & availability^^ to personal data in a timely manner in the event of a physical or technical incident.
- A key principle of GDPR is that you process personal data ^^securely by means of "appropriate technical & organisational measures"^^ - this is the "security principle".
- The GDPR sets out several key principles: #card
card-last-interval:: 9.28
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-24T02:20:42.714Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:20:42.715Z
card-last-score:: 5
- What is Data Protection? #card
card-last-interval:: 11.34
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.56
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-26T00:46:23.031Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:46:23.032Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Data Protection is about an ^^individual's fundamental right to privacy.^^
- When an individual gives their personal data to any organisation, the recipient has the duty to keep the data both safe & private. This applies to both printed & electronic data.
- What does Data Protection Legislation do? #card
card-last-interval:: 19.01
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.18
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-03T16:40:10.475Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:40:10.475Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Data Protection Legislation:
- governs the way we deal with personal data / information
- provides a mechanism for safeguarding the privacy rights of individuals in relation to the processing of their data
- upholds rights and enforces obligations
- Data Protection Legislation:
- What is Personal Data? #card
card-last-interval:: 29.26
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-13T22:47:49.984Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:47:49.984Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Personal Data is any information relating to an identified or ^^identifiable natural person^^ ("data subject").
- What is an identifiable natural person? #card
card-last-interval:: 23.43
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-08T02:44:34.994Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:44:34.995Z
card-last-score:: 5
- An identifiable natural person is one who can be identified, directly or indirectly, in particular by reference to an identifier such as a name, an identification number, location data, an online identifier to one or more factors specific to the ^^physical, physiological, genetic, mental, economic, cultural, or social identity^^ of that natural person.
- What is Data Processing? #card
card-last-interval:: 54.82
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2023-01-08T15:21:19.993Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:21:19.993Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Data Processing is ^^performing any operation on personal data^^, either manually or by automated means, including:
- Obtaining
- Storing
- Transmitting
- Recording
- Organising
- Altering
- Disclosing
- Erasing
- Data Processing is ^^performing any operation on personal data^^, either manually or by automated means, including:
-
Entities in GDPR
- GDPR distinguishes between:
- The Data Subject
- The Data Protection Officer (DPO)
- The Data Controller
- The Data Processor
- What is the Data Subject? #card
card-last-interval:: 33.64
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.9
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-18T07:52:24.372Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:52:24.372Z
card-last-score:: 5
- The Data Subject is the person to whom the data relates.
- GDPR only applies to living individuals, but any duty of confidence in place prior to the death extends beyond that point.
- In Ireland, the next of kin of the deceased are entitled to a Freedom of Information request to the deceased's personal data.
- What is the DPO? #card
card-last-interval:: 11.34
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.56
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-26T00:46:36.130Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:46:36.130Z
card-last-score:: 5
- The primary role of the Data Protection Officer (DPO) is to ^^ensure that their organisation processes the personal data of its staff, customers, and other data subjects in compliance with the applicable data protection rules.^^
- The Data Protection officer is required to be an expert within this field, along with the requirement for them to report to the highest management level.
- With this being a challenging aspect of GDPR compliance for smaller organisations, there is the option to make an external appointment of a third-part DPO.
- When is the DPO a mandatory role? #card
card-last-interval:: 9.28
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-23T22:35:00.574Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:35:00.574Z
card-last-score:: 5
- The DPO is a mandatory role within 3 different scenarios:
-
- When the processing is undertaken by a public authority or body.
-
- When an organisation's main activities require the frequent & large-scale monitoring of individual people.
-
- Where large-scale processing of special categories of data or data relating to criminal records forms the core activities.
-
- The DPO is a mandatory role within 3 different scenarios:
- What is the Data Controller? #card
card-last-interval:: 9.68
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-24T08:43:13.191Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:43:13.191Z
card-last-score:: 5
- The Data Controller is the company or an individual who ^^has overall control over the processing of personal data.^^
- The Data Controller takes on the responsibility for GDPR compliance.
- A Data Controller needs to have had sufficient training and to be able to competently ensure the security & protection of data held within the organisation.
- What is the Data Processor? #card
card-last-interval:: 4.28
card-repeats:: 2
card-ease-factor:: 2.56
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-23T00:35:18.504Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-18T18:35:18.505Z
card-last-score:: 5
- The Data Processor is the person who is ^^responsible for the processing of personal information.^^
- Generally, this role is undertaken under the instruction of the data controller.
- This might mean obtaining or recording the data, its adaption, and use. It may also include the disclosure of the data or making it available to others.
- Generally, the Data Processor is involved in the more technical elements of the operation, while the interpretation & main decision-making is the role of the Data Controller.
- GDPR distinguishes between:
-
Cloud Services & GDPR
- What makes a Cloud Service Provider a Data Processor? #card
card-last-interval:: 23.43
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-08T06:06:16.813Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:06:16.814Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A Cloud Service Provider will be considered a Data Processor under GDPR if it provides data processing services (e.g., storage) on behalf of the Data Controller ^^even without determining the purposes & means of processing.^^
- A Cloud Service Provider that offers personal data processing services directly to Data Subjects will be considered a Data Controller.
- What makes a Cloud Service Provider a Data Processor? #card
card-last-interval:: 23.43
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-08T06:06:16.813Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:06:16.814Z
card-last-score:: 5
- What are some key benefits of GDPR for Data Subjects? #card
collapsed:: true
card-last-interval:: 19.01
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.18
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-03T16:40:34.643Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:40:34.643Z
card-last-score:: 5
- More information must be given to data subjects (e.g., how long the data will be kept, right to lodge a complaint).
- The Data Controller must explain & document the legal basis for processing the personal data.
- GDPR tightens the rules on how consent can be obtained.
- Must be distinguishable from other matters and in clear, plain language.
- It must be as easy to withdraw consent as it is to give it.
- Mandatory notification of security breaches without "undue delay" to the Data Protection Commissioner (within 72 hours).
- What are some key rights of Data Subjects? #card
card-last-interval:: 41.44
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.18
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-26T06:18:29.246Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:18:29.246Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Right of Access (copy to be provided within one month)
- Right to Erasure (the right to be forgotten)
- Right to Restriction of Processing
- Right to Object to Processing
- Right not to be subject to a decision based solely upon automated processing
- What are Personal Data Security Breaches? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-17T15:32:03.843Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-20T08:32:03.844Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Personal Data Security Breaches include:
- Disclosure of confidential data to unauthorised individuals.
- Loss or theft of data or equipment upon which data is stored.
- Hacking, viruses, or other security attacks on IT equipment / systems / networks.
- Inappropriate access controls allowing unauthorised use of information.
- Emails containing personal data sent in error to the wrong recipient.
- Personal Data Security Breaches apply to both paper & electronic records.
- Personal Data Security Breaches include:
- What is GDPR? #card
card-last-interval:: 56.69
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2023-01-07T03:40:11.348Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-11T11:40:11.348Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
HTTP Cookies
- What is a (HTTP) Cookie? #card
card-last-interval:: 9.28
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-23T22:35:54.977Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:35:54.977Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A (HTTP) Cookie is a small piece of data stored on the user's computer by the web browser while browsing a website.
- Cookies were designed to be a reliable mechanism for websites to remember stateful information (such as items in the shopping cart in an online store) or to record the user's browsing activity.
- They can be also be used to remember pieces of information that the user previously entered into form fields.
- Authentication Cookies are the most common method used by web servers to know whether the user is logged in or not, and which account they are logged into.
-
Cookie Implementation
- How are cookies implemented? #card
card-last-interval:: 2.8
card-repeats:: 2
card-ease-factor:: 2.6
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-17T11:27:17.132Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:27:17.133Z
card-last-score:: 5
- Cookies are ^^arbitrary pieces of data^^ (i.e., large, random strings), usually chosen & first sent by the web server, and stored on the client computer by the web browser.
- The browser then sends them back to the server with every request.
- Browsers are required to: #card
card-last-score:: 5
card-repeats:: 2
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-17T11:25:54.217Z
card-last-interval:: 2.8
card-ease-factor:: 2.6
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:25:54.218Z
- support cookies as large as 4,906 bytes in size
- support at least 50 cookies per domain
- support at least 3,000 cookies in total
- How are cookies implemented? #card
card-last-interval:: 2.8
card-repeats:: 2
card-ease-factor:: 2.6
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-17T11:27:17.132Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:27:17.133Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Cookie Structure
- What are the components of a cookie? #card
card-last-interval:: 8.35
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.46
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-29T21:09:38.375Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-21T13:09:38.376Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A cookie consists of the following components:
- Name
- Value
- Zero or more attributes (name - value pairs). These attributes store information such as the cookie's expiration, domain, and flags (such as Secure and HttpOnly)
- A cookie consists of the following components:
- What are the components of a cookie? #card
card-last-interval:: 8.35
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.46
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-29T21:09:38.375Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-21T13:09:38.376Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Session Cookies
- What is a session cookie? #card
card-last-interval:: 19.01
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.18
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-03T16:40:31.570Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:40:31.571Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A session cookie (aka in-memory cookie, transient cookie, or non-persistent cookie) is a cookie that ^^exists only in temporary memory while the user navigates its website.^^
- Web browsers normally delete session cookies when the user closes the browser.
- Session cookies do not have an expiration date assigned to them, which is how the browser know to treat them as session cookies.
- What is a session cookie? #card
card-last-interval:: 19.01
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.18
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-03T16:40:31.570Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:40:31.571Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Persistent Cookies
- What is a persistent cookie? #card
card-last-interval:: 23.43
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-04T21:33:28.732Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-11T11:33:28.733Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A persistent cookie is a cookie which ^^expires at a specific data or after a specific length of time.^^
- A persistent cookie's information will be transmitted to the server every time the user visits the website that the cookie belongs to, for the lifespan of the persistent cookie (as set by its creator), or every time that the user views a resource belonging to that website from another website (such as an advertisement).
- Persistent cookies are sometimes referred to as tracking cookies because they can be used by advertisers to record information about a user's web browsing habits.
- However, tracking cookies are mainly used for legitimate reasons, such as keeping users logged into their accounts on website to avoid re-entering login credentials at every visit.
- What is a persistent cookie? #card
card-last-interval:: 23.43
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.42
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-04T21:33:28.732Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-11T11:33:28.733Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Cookie Attributes
- Consider the following response header sent by a webserver that contains 3 persistent cookies:
- What do the Domain and Path attributes do? #card
card-last-interval:: 9.28
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-18T18:45:59.521Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-09T12:45:59.521Z
card-last-score:: 3
- The Domain and Path attributes define the cookie's scope.
- What does the Secure attribute do? #card
card-last-interval:: 84.1
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.76
card-next-schedule:: 2023-02-06T22:21:24.146Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:21:24.147Z
card-last-score:: 5
- The Secure attribute ensures that the cookie can only be transmitted over an encrypted connection, making it a "secure cookie".
- What does the HttpOnly attribute do? #card
card-last-interval:: 64.01
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.52
card-next-schedule:: 2023-01-24T13:10:00.242Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-21T13:10:00.242Z
card-last-score:: 5
- The HttpOnly attribute ^^directs cookies not to expose cookies through channels other than HTTP / HTTPS.^^
- This means that this HttpOnly cookie cannot be accessed via client-side scripting languages (notably JavaScript).
- What is a (HTTP) Cookie? #card
card-last-interval:: 9.28
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.32
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-23T22:35:54.977Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:35:54.977Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
GDPR & Cookies
- Generally, a user's consent must be sought before a cookie is installed in a web browser.
- There are two expemptions:
- The Communications Exemption
- The Strictly Necessary Exemption
- What is the Communications Exemption? #card
card-last-interval:: 41.44
card-repeats:: 5
card-ease-factor:: 2.18
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-26T06:18:30.530Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:18:30.530Z
card-last-score:: 5
- The Communications Exemption applies to cookies ^^whose sole purpose is for carrying out the transmission of a communication over a network^^, for example, to identify the communication endpoints.
- Cookies that meet these criteria are exempted from being required to ask for the user's consent prior to installation.
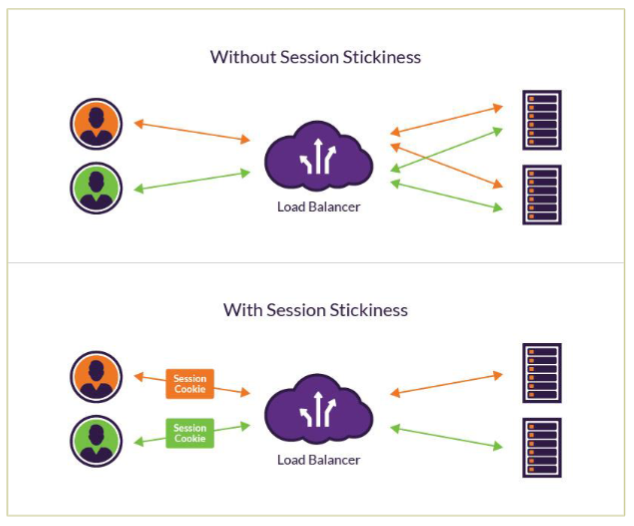
- Example: load-balancing cookies that distribute network traffic across different backend servers, also known as session stickiness.
- Here, a load-balancer creates an affinity between a client and a specific network server for the duration of a session using a cookie with a random & unique tracking ID.
- Subsequently, the load-balancer routes all the of the requests from this client to a specific backend server using the tracking ID, for the duration of the session.
 {:height 426, :width 529}
{:height 426, :width 529}
- What is the Strictly Necessary exemption? #card
card-last-interval:: 28.3
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.66
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-17T15:34:39.740Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-10-20T08:34:39.740Z
card-last-score:: 5
- The Strictly Necessary exemption exempts cookies that are strictly necessary to provide the service of delivered over the internet, i.e., a website or app from being required to ask the user's consent prior to installation.
- ^^This service must have been explicitly requested by the user (i.e., typing in the URL), and the use of the cookie must be restricted to what is strictly necessary to provide that service.^^
- Cookies related to advertising are not strictly necessary, and must be consented to.
- Examples:
- A website uses session cookies to keep track of items that a user places in an online shopping basket (assuming that this cookie will be deleted once the session is over).
- Cookies that a record a user's language or country preference.

