5.6 KiB
5.6 KiB
- #CT255 - Next Generation Technologies II
- Previous Topic: DIffie-Hellman Key Exchange
- Next Topic: Message Authentication
- Relevant Slides:
-
Block Ciphers
-
Encryption Algorithms Based on Block Ciphers
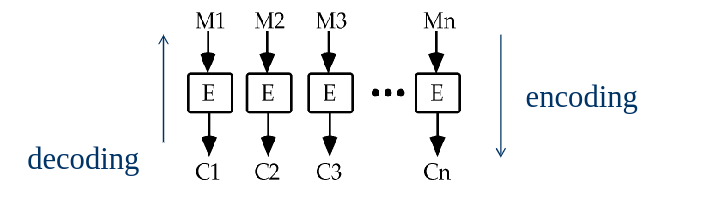
collapsed:: true- In a block cipher, the message is broken into blocks
M1,M2, etc., ofKbits length, each of which is then encrypted. - Claude Shannon suggested to use the two primitive cryptographic operations as building blocks for such ciphers:
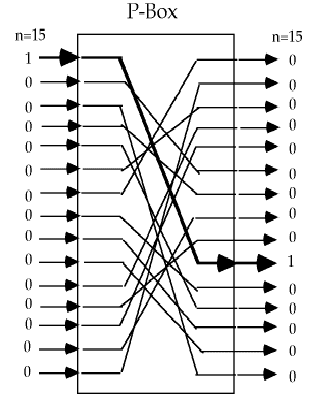
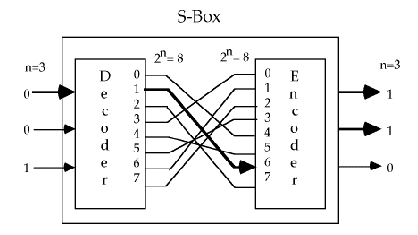
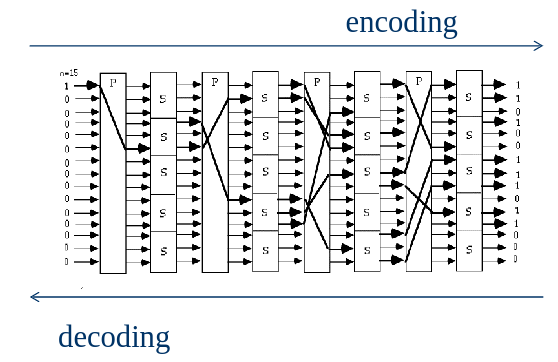
- Substitution.
- Permutation.
-
The Permutation Operation
-
The Substitution Operation
-
Substitution-Permutation Network
- In a block cipher, the message is broken into blocks
-
Confusion & Diffusion
- A cipher needs to completely obscure the statistical properties of the original message.
- Shannon introduced two terms to describe this:
- Diffusion seeks to make the statistical relationship between the plaintext & ciphertext as complex as possible.
- Confusion seeks to make the relationship between the statistics of the ciphertext and the value of the encryption key as complex as possible.
- Both thwart attempts to deduce the key used via a cryptanalysis.
-
Reversible Transformation
- An important block cipher principle is Reversible Transformation - transformations must be reversible or non-singular.
- There must be a 1:1 association between an $n$-bit plaintext and an $n$-bit ciphertext, otherwise mapping is irreversible.
-
Features of Private-Key Cryptography
- Traditional private/secret/single key cryptography uses one key, shared by only the sender and the receiver.
- The algorithm/cipher itself is public, i.e., not a secret.
- If the key is disclosed, communications are compromised.
- The key is also symettric, parties are equal.
- Hence, methods doe do not protect the sender from receiver forging .
- Examples include DES and AES.
-
AES
- The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is the successor of DES.
- It is a modern block cipher with 128 bits block length.
- Uses 128, 192, or 256 bit long keys.
- The de-facto standard for secure encryption.
- Widely used for file/data encryption, and secure network communication.
-
Why does Block & Key length matter?
- Cryptographic algorithms with short block length can be tackled easily.
- Large keys & long blocks prevent brute force attacks
- The DES cipher used 56-bit keys - The generally accepted minimum key length today is 128-bit.
-
Brute Force Attacks
- Always possible to simply try every key.
- Most basic attack, effort proportional to key size.
- Assume that you either know or recognise plaintext.
-
The Feistel Cipher
- In practice, we need to be able to decrypt messages as well as encrypt them. Hence we either need to define inverses for each of the S & P-boxes (but this doubles the code / hardware needed) or define a structure that is easy to reverse, so you can use basically the same code or hardware for both encryption & decryption.
- A Feistel Cipher is such a structure that is easy to reverse.
- It is based on the concept of the invertible product cipher.
- Most symmetric block ciphers are based on a Feistel Cipher structure.
- Feistel invented a suitable structure which adapted Shannon's S-P network into an easily invertible structure.
- Essentially, the same hardware or software is used for both encryption & decryption, with just a slight change in how the keys are used.
-
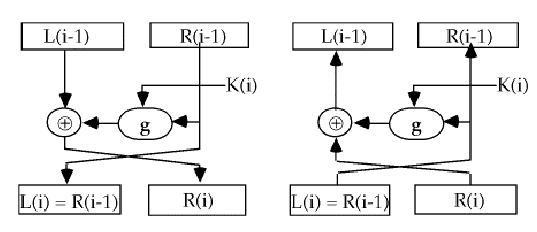
A Single Round
collapsed:: true- The idea is to partition the input block into two halves,
L(i-1)&R(i-1), and use onlyR(i-1)in thei^{\text{th}}round (part) of the cipher. - The function
gincorporates one stage of the S-P network, controlled by part of the keyK(i)known as thei^{\text{th}}subkey. 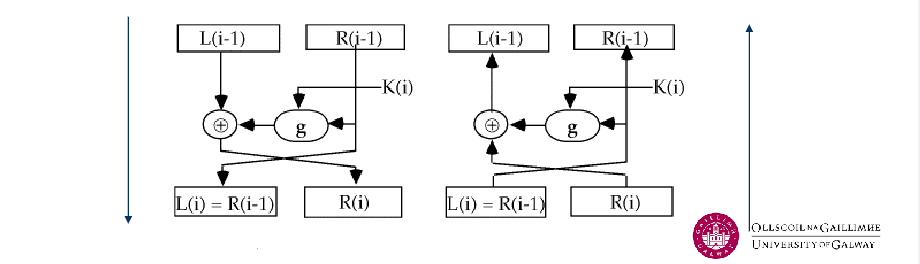
- A round of a Feistel Cipher can be described functionally as:
- The idea is to partition the input block into two halves,
-
A Feistel Network
- Perform multiple transformation (single rounds) sequentially, whereby the output of the $i$^{th} round becomes the input of the $(i+1)$^{th} round.
- Every round gets its own subkey, which is derived from the master key.
- The decryption process goes from bottom to top.
-
Feistel Cipher Design Elements
- Block size.
- Key size.
- Number of rounds.
- Subkey generation algorithm.
- Round function.
- Fast software encryption / decryption.
-