5.1 KiB
5.1 KiB
- #CT255 - Next Generation Technologies II
- Previous Topic: Introduction to Cryptography
- Next Topic: Hash Cracking Using Rainbow Tables
- Relevant Slides:
- What is a password? #card
card-last-interval:: 10.6
card-repeats:: 3
card-ease-factor:: 2.56
card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-25T06:28:38.024Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T16:28:38.024Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A password is a memorised secret used to confirm the identity of a user.
- Typically, an arbitrary string of characters including letters, digits, or other symbols.
- A purely numeric secret is called a Personal Identification Number (PIN).
- The secret is memorised by a party called the claimant while the party verifying the identity of the claimant is called the verifier.
- The claimant & the verifier communicate via an authentication protocol.
- A password is a memorised secret used to confirm the identity of a user.
-
Some Password Alternatives
- One-Time Password (OTP).
- Transaction Authentication Number (TAN) list used for online banking - they can only be used once.
- Time-synchronised one-time passwords.
- Biometric methods.
- Fingerprints, irises, voice, face.
- Cognitive passwords.
- Use question & answer cue/response pairs to verify identity.
- One-Time Password (OTP).
-
Algorithmic Generation of OTP
- Paper-based TANs are hard to manage -> both the claimant and the verifier need to have a copy of every OTP (possibly hundreds of them).
- Idea: each OTP may be created from the passt OTPs used.
- An example of this type of algorithm, credited to Leslie Lamport, uses a one-way function (hash function).
-
One-Way Functions
- What is a hash function? #card
card-last-interval:: 29.99
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.56
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-14T19:04:01.691Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:04:01.691Z
card-last-score:: 5
- A one-way function
Hproduces a fixed-size outputhbased on a variable size inputs.-
H(s) = h
-
His also called a hash function,his called a hash (value).- Important: one-way property:
- For a given hash code
h, it is infeasible to findsthatH(s) = h.
- For a given hash code
- A one-way function
-
Leslie Lamport's Algorithm #card
card-last-interval:: 7.8 card-repeats:: 3 card-ease-factor:: 2.46 card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-22T15:17:39.453Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:17:39.454Z card-last-score:: 5- For every claimant, a random seed (starting value)
sis chosen. - A hash function
H(s)is applied repeatedly (e.g., 1,000 times) to the seed, giving a value of:-
H(H(H(...(H(s)....))))
-
- The user's first login uses an OTP
pderived by applyingH999 times to the seed, i.e.,H^{999}(s). - The verifier can authenticate that this is the correct OTP, because
H(p) = H^{1000}(s), the value stored. - The value stored is then replaced by
pand the user is allowed to log in. - The next login must be accompanied by
H^{998}(s). - Again, this can be validated because hashing gives
H^{999}(s)which isp, the value stored after the previous login. - The new value replaces
pand the user is authenticated. - This process can be repeated another 997 times, each time the password will be
Happlied one fewer times.
- For every claimant, a random seed (starting value)
-
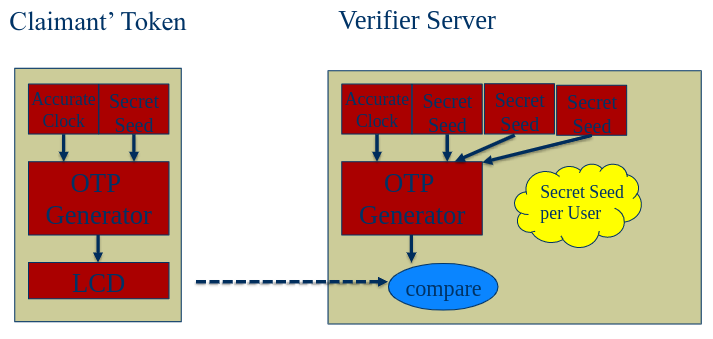
Time-Synchronised OTP #card
card-last-interval:: 8.63 card-repeats:: 3 card-ease-factor:: 2.46 card-next-schedule:: 2022-11-20T02:38:06.966Z card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-11T11:38:06.967Z card-last-score:: 5
- What is a hash function? #card
card-last-interval:: 29.99
card-repeats:: 4
card-ease-factor:: 2.56
card-next-schedule:: 2022-12-14T19:04:01.691Z
card-last-reviewed:: 2022-11-14T20:04:01.691Z
card-last-score:: 5
-
Some New Biometric Methods
- Hand geometry: Measurement & comparison of the (unique) different physical characteristics of the hand.
- Palm vein authentication: Uses an infrared beam to penetrate the user's hand as it is waved over the system; the veins within the palm are returned as black lines.
- Retina scan: Provides an analysis of the capillary blood vessels located in the back of the eye.
- Iris scan: Provides an analysis of the rings, furrows, & freckles in the coloured ring that surrounds the pupil of the eye.
- Face recognition, signature, & voice analysis.
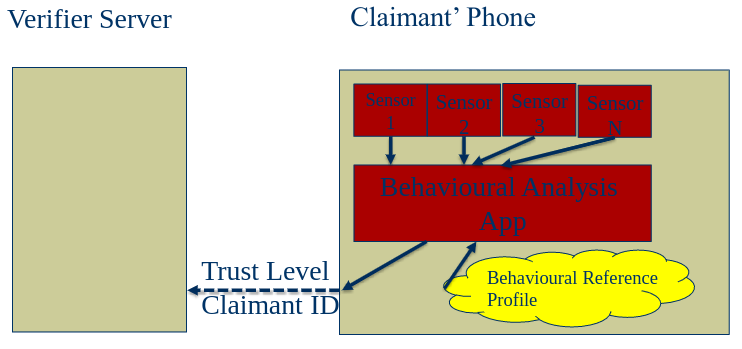
- Behavioural biometrics:
-
Multi-Factor Authentication
- This may include a combination of the following:
- Some physical object in the possession of the user, e.g., a USB stick with a secret token, a bank card, a key, etc.
- Some secret known only to the user, such as a password, PIN, TAN, etc.
- Some physical characteristic of the user (biometrics), such as a fingerprint, eye iris, voice, typing speed, pattern in key press intervals, etc.
- Somewhere you are, such as connection to a specific computing network or utilising a GPS signal to identify the location.
- This may include a combination of the following: